Major points:
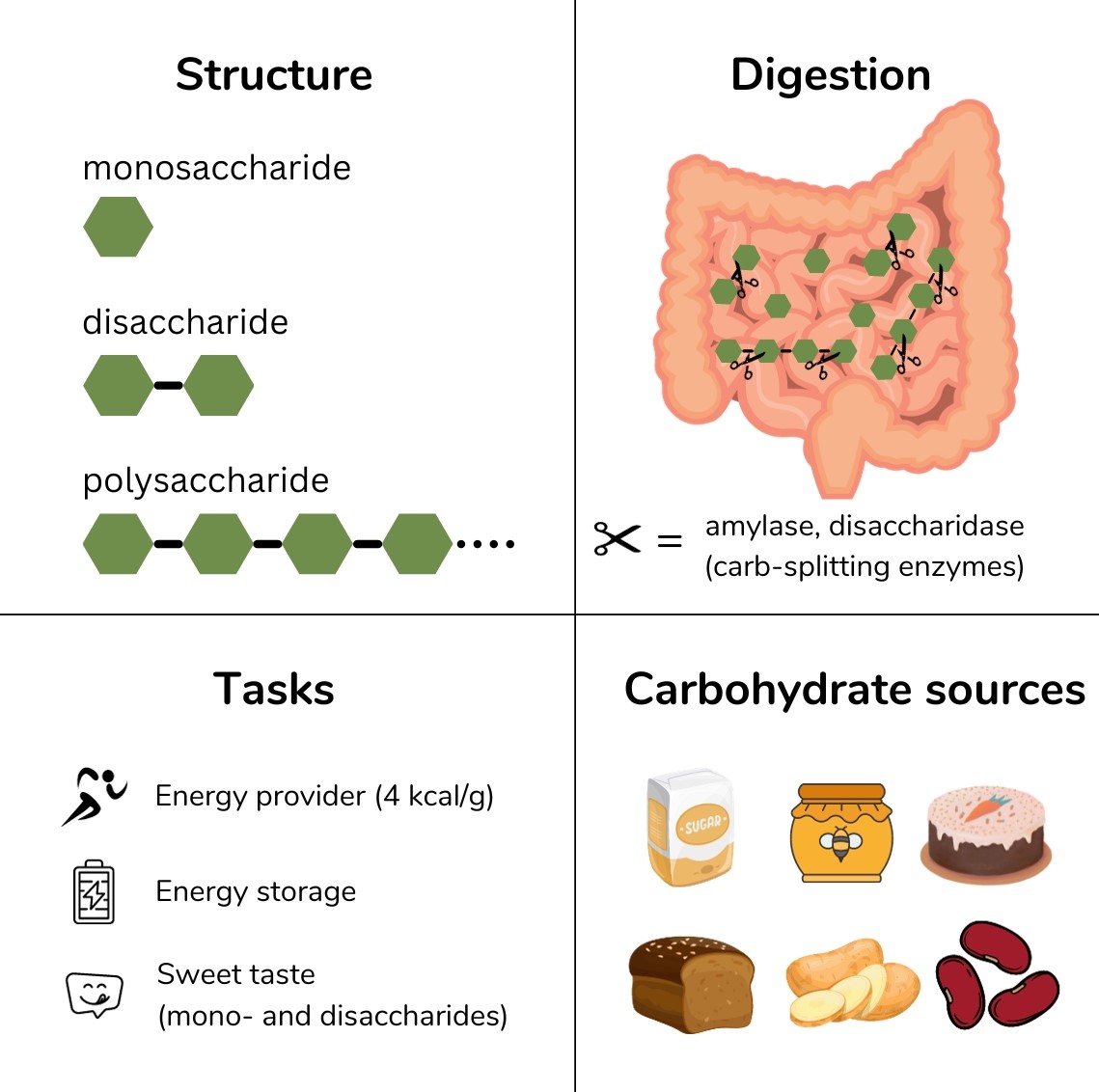
- Carbohydrates belong to the group of macronutrients and occur naturally as mono-, di-, or polysaccharides.
- Carbohydrates provide energy that is available to the body more quickly than the energy from protein or fat.
- Neatic restricts only mono- and disaccharides added to foods; all other carbohydrates (e.g. in fruit, milk, grain, potatoes, and legumes) are allowed without restriction.
What are carbohydrates?
Along with protein and fat, carbohydrates are the main suppliers of energy. The energy from carbohydrates is more rapidly available to the body than energy from protein or fat.
Carbohydrates are divided into three different groups:
- Monosaccharides are glucose, fructose, and galactose. These are found in fruit, juices, and honey.
- Disaccharides are malt sugar (maltose), household sugar (sucrose), and milk sugar (lactose). These occur in milk and granulated sugar. Disaccharides always consist of two linked monosaccharides.
- Polysaccharides are long sugar chains such as starch or glycogen. They consist of several monosaccharides linked together. Polysaccharides are found in grain (e.g. wheat, spelt, rye, barley, oats, rice, corn, millet), legumes (e.g. beans, peas, peanuts, lentils), and potatoes. Foods made from these ingredients, such as bread, rolls, pasta, fried potatoes, French fries, and mashed potatoes, are also rich in polysaccharides. They do not taste sweet.
How are carbohydrates digested?
Di- and polysaccharides are composed of glucose, fructose, and galactose. To use the energy from carbohydrates, the body must first break them down into monosaccharides via the enzymes disaccharidase (for disaccharides) and amylase (for polysaccharides). Disaccharides are each cleaved once, resulting in two monosaccharides. Polysaccharides must be cleaved more often to obtain monosaccharides.
What does the body need carbohydrates for?
- They provide the body with energy (4 kcal/g)
- They store energy, especially in the liver and muscle in the form of glycogen
- They have a sweet taste (mono- and disaccharides)
What does Neatic recommend concerning carbohydrates?
Polysaccharides can be eaten in Neatic without restrictions. Only mono- and disaccharides that are added to foods should be avoided. This includes table sugar, glucose, and fructose, as well as sugars that are naturally present in honey, syrups, fruit juices, and fruit juice concentrate.
Fruit, on the other hand, is allowed as long as it is eaten in its “edible entirety.” By “edible entirety” Neatic means that all edible components are eaten completely, e.g. an apple with the peel or eating an orange whole instead of squeezing it.
Does the low carb diet helps with weight loss? Find out more here.
Bibliography:
Höfler, Elisabeth; Sprengart, Petra (2018): Praktische Diätetik. Grundlagen, Ziele und Umsetzung der Ernährungstherapie. 2., überarbeitete und erweiterte Auflage. Stuttgart: WVG, Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft.

