Major points:
- Protein belongs to the macronutrients and is classified according to animal or plant origin.
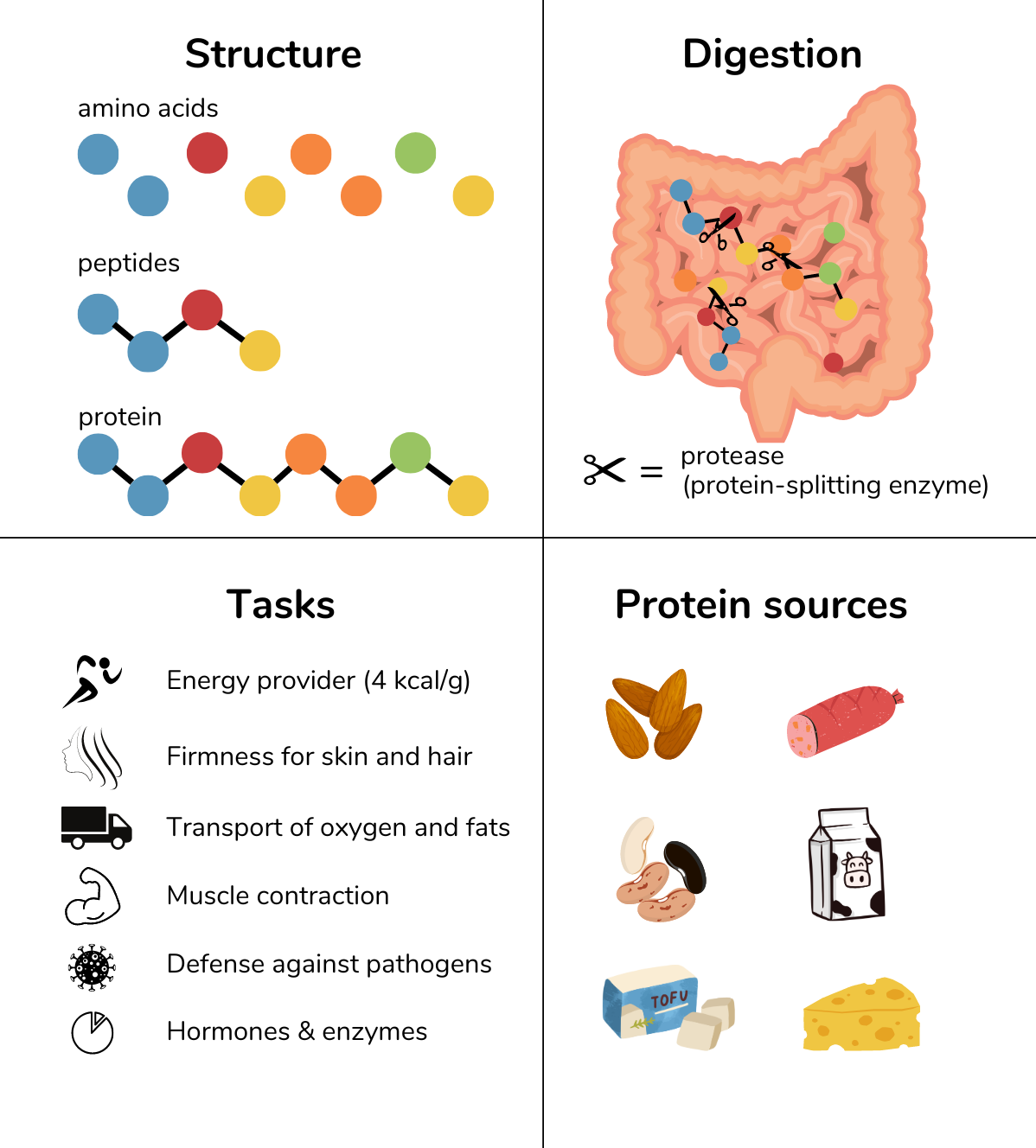
- Protein provides energy and structure to body tissues, transports oxygen in the blood, enables muscle contraction and immune response, and forms the basis of numerous hormones and enzymes.
- Neatic does not limit the quantity or selection of protein.
What is protein?
Protein is found in every cell in the body. Protein consists of many individual building blocks called amino acids. Amino acids are always linked together in the same way. Chains of up to 100 amino acids are called peptides, longer chains are called proteins.
The human body can use 20 different amino acids to build protein. Of the 20 amino acids, nine are essential. This means that the body cannot produce these nine amino acids itself. Therefore, they must be ingested through food. The other eleven amino acids can be built by the body of a healthy person.
Protein is found in many different foods
- Animal foods (e.g. eggs, meat, fish, milk, and cheese)
- Plant foods (e.g. tofu, nuts, beans, lentils, and peas)

Protein digestion
Protein digestion begins in the stomach. There, proteins are denatured so that they can be broken down into individual amino acids by proteases (enzymes) in the small intestine.
Protein functions
Protein performs many different functions in the body…
- it provides energy (4 kcal/g)
- as collagen it gives skin and hair firmness
- as hemoglobin and lipoproteins it transports oxygen and fats in the blood
- as myosin it is an important component of muscle movement
- as antibodies it fights pathogens in the body
- as a hormone (e.g. insulin and glucagon) it regulates important body functions
- as an enzyme (e.g. lactase and lipase) it digests food components
What does Neatic recommend concerning protein?
Neatic does not limit the amount or choice of protein. However, be cautious with processed foods since they may contain flavors, sweeteners, and sugar. Examples include marinated meats, various types of sausages, cheese preparations with herbs or spices, as well as plant-based meat and cheese products. Shakes, bars, and puddings that advertise “extra protein” almost always contain taste seducers.
Everything you need to know about protein quality can be found here.
Bibliography:
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Ernährung e.V. (2021): Ausgewählte Fragen und Antworten zu Protein und unentbehrlichen Aminosäuren. Available online at https://www.dge.de/wissenschaft/weitere-publikationen/faqs/protein/?L=0, checked on 2/10/2022.
Elmadfa, Ibrahim; Muskat, Erich; Fritzsche, Doris; Meyer, Alexa Leonie (2019): Nährwert-Kalorien-Tabelle, Die große GU. Neuausgabe 2020/21. München: GRÄFE UND UNZER Verlag GmbH.
Höfler, Elisabeth; Sprengart, Petra (2018): Praktische Diätetik. Grundlagen, Ziele und Umsetzung der Ernährungstherapie. 2., überarbeitete und erweiterte Auflage. Stuttgart: WVG, Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft.
Leitzmann, Claus; Keller, Markus (2020): Vegetarische und vegane Ernährung. 4., vollständig überarbeitete und erweiterte Auflage. Stuttgart: Verlag Eugen Ulmer.
Max Rubner-Institut (2008): Nationale Verzehrsstudie II. Ergebnisbericht, Teil 2. Die bundesweite Befragung zur Ernährung von Jugendlichen und Erwachsenen. Available online at https://www.bmel.de/SharedDocs/Downloads/DE/_Ernaehrung/NVS_ErgebnisberichtTeil2.pdf;jsessionid=9D48DD3B81AA52123DD134242DF6DC3A.live922?__blob=publicationFile&v=2, checked on 6/01/2021.
